
Fixed Overhead Volume Variance is necessary in the preparation of operating statement under absorption costing as it removes the arithmetic duplication as discussed earlier. Further analysis might reveal that the positive variance is a symptom of larger issues such as suboptimal sales forecasting or marketing misalignment. Conversely, a negative variance, which points to higher than expected production levels, could signal market share growth or an unexpected surge in demand. However, it could also raise concerns about overextension of resources and the potential for increased wear and tear on machinery, which could lead to higher maintenance costs or capital expenditures in the long term.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
On the other hand, the budgeted production volume is the production volume that the company estimates to produce or achieve during the period. It is the normal capacity that the company or the existing facility can achieve for the period. This figure is usually included in the budget of production that is planned or scheduled before the production starts. Actual production volume is the production that the company actually achieves (in hours) or produces (in units) during the period. The figure in hours here can either be labor hours or machine hours depending on which one is more suitable for the measurement in the production.
- If the fixed overhead cost applied to the actual production using the standard fixed overhead rate is bigger than the budgeted fixed overhead cost, the fixed overhead volume variance is the favorable one.
- The journal above now allocates some of this expense (11,000) to production, this is represented by the credit entry to the expense account.
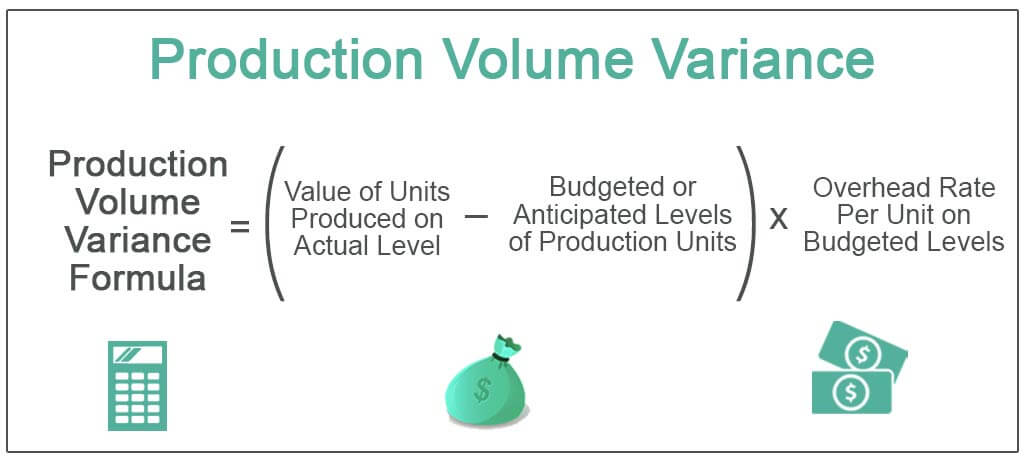
- Fixed overhead volume variance is the difference between the amount budgeted for fixed overhead costs based on production volume and the amount that is eventually absorbed.
- Graph 4 shows a situation where both actual activity and actual overhead expenditure differ from budget.
- In practice other measures of activity, in particular direct labour hours (DLHs), are used as an absorption base.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
AccountingTools
However, the actual number of units produced is only 2,000, resulting in a total of $50,000 fixed overhead costs. This variance would be posted as a debit to the fixed overhead volume variance account. Fixed overhead volume variance refers to the difference between the budgeted fixed overheads and the actual overheads applied to the units produced during an accounting period. The variance value reflects the over or under absorption of fixed overheads, and it arises due to a change in the quantum of production against the budgeted quantum of production. When standard hours exceed normal capacity, the fixed factory overhead costs are leveraged beyond normal production. The fixed factory overhead volume variance is the difference between the budgeted fixed overhead at normal capacity and the standard fixed overhead for the actual units produced.
Overhead Variances
This results in $12,000 of overhead being absorbed and consequent over absorption of overhead by $2,000. By contrast, efficiency variance measures efficiency in the use of the factory (e.g., machine hours employed in costing overheads to the products). Controlling overhead costs is more difficult and complex than controlling direct materials and direct labor costs. Fixed Overhead Volume Variance is the difference between the fixed production cost budgeted and the fixed production cost absorbed during the period.
How do we calculate the total overhead cost variance?
For simplicity assume that there was no fixed overhead expenditure variance, that is that actual overhead expenditure was as budgeted. Estimate the total number of standard direct labor hours that are needed to manufacture your products during 2023. Budget or spending variance is the difference between the budget and the actual cost for the actual hours of operation.
4: Factory overhead variances
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own.
This metric is particularly useful for management accountants who are tasked with monitoring internal cost controls and operational performance. By integrating this variance into financial reports, analysts can provide a comprehensive overview of how effectively a company is leveraging its production capacity. The fixed overhead costs that are a part of this variance are usually comprised of only those fixed costs incurred in the production process. Examples of fixed overhead costs are factory rent, equipment depreciation, the salaries of production supervisors and support staff, the insurance on production facilities, and utilities.
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for is a check considered cash or accounts payable convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
When a company observes a variance from its expected fixed overhead, it’s not merely looking at a discrepancy in numbers but also at underlying factors that may include shifts in market conditions or internal process changes. For instance, a positive variance often prompts a review of market engagement strategies, as it may suggest that the company’s products are not meeting market demand as anticipated. Graph 3 shows a situation where actual activity is greater than budgeted activity and actual overhead expenditure is as budgeted.
This distinction is important for managers who need to make informed decisions about resource allocation, budget adjustments, and process improvements. Explore the significance of fixed overhead volume variance in shaping financial strategies and enhancing business planning efficiency. Therefore, these variances reflect the difference between the Standard Cost of overheads allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual overhead cost incurred. Using the information given below, compute the fixed overhead cost, expenditure, and volume variances. This situation is shown in graph 7 where actual overhead expenditure is the same as budgeted and actual production is 1,000 units.
Commentaires récents